In this article, we will demystify the concept of SSDs and shed light on why they have become the superior choice over traditional hard-disk drives (HDDs). Whether you’re a business professional, web designer, or website owner, understanding the benefits of SSD storage for web hosting can be extremely useful. So, let’s embark on a journey to uncover the power and advantages of SSD storage and the reasons behind their dominance over traditional HDDs.
Table of Contents
What Is SSD Storage: Exploring Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
Solid-State Drives, commonly known as SSDs, are a type of storage device that has transformed the way we store and access data. Unlike traditional hard drives, which use spinning platters and mechanical read/write heads, SSDs leverage flash memory technology. Flash memory, made up of memory chips, provides a storage device that retains data even when the power is turned off. The absence of moving parts in SSDs translates to faster read and write speeds, enhanced reliability, and improved overall performance.
A History of Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
The history of SSDs dates back several decades, with the first commercial flash-based SSD introduced in the early 1990s. However, due to their high production costs and limited storage capacities, SSDs remained a niche product for many years. As technology advanced and economies of scale kicked in, the cost of flash storage decreased, resulting in improved affordability and larger storage space. Today, SSDs have become the storage solution of choice for a wide range of applications, including web hosting, due to their remarkable performance and reliability.
Solid-State Storage for Web Hosting: Why SSDs Outperform HDDs
When it comes to choosing a web hosting company, the choice between SSD and HDD storage is pivotal. SSDs have gained significant popularity in the hosting industry due to their undeniable advantages over hard disk drives (HDDs). Let’s explore why SSDs outperform HDDs in the realm of web hosting:
By utilizing SSD storage, you can improve your website’s loading speed and potentially boost its SEO performance
- Speed and Performance: SSDs offer lightning-fast data access and transfer speeds, thanks to their ability to read and write data at a much higher rate compared to HDDs. With faster loading times, your website visitors will have a seamless browsing experience, resulting in higher user satisfaction and engagement. Additionally, SSDs excel in handling concurrent requests and heavy workloads, making them ideal for websites with high traffic volumes. According to Avast, a typical HDD can deliver a read/write speed of 30 to 150 MB per second, while a typical SSD can deliver a read/write speed of up to 500 MB per second.
- Reliability and Durability: Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts making them more resistant to mechanical failures and physical damage. This inherent durability ensures that your data remains safe and accessible even in harsh environments. With SSD-powered hosting, you can have peace of mind knowing that your valuable business data is protected.
- Energy Efficiency: SSDs consume significantly less power than HDDs. This energy efficiency not only reduces your carbon footprint but also results in lower operating costs for web hosting infrastructure. By choosing a hosting plan with SSD storage, you contribute to a greener environment while optimising your resource allocation.
- Improved Loading Times: In today’s fast-paced digital world, loading times can make or break your online presence. Studies have shown that even a few seconds of delay can lead to increased bounce rates and decreased conversions. With SSD storage, your website’s files and data are retrieved and delivered at an accelerated pace, ensuring that your visitors have a seamless browsing experience and stay engaged with your content.
- Enhanced SEO Performance: Search engines, like Google, take website loading speed into consideration when ranking search results. Websites that load faster tend to have a competitive advantage in search engine optimisation (SEO). By utilising SSD storage, you can improve your website’s loading speed and potentially boost its SEO performance, leading to increased visibility and organic traffic.
With the above points in mind, you should now see why it’s important to opt for a web hosting company that offers SSD storage, like MCloud9. Additionally, with perks like LiteSpeed web server, cPanel control panel, and a complimentary .co.za domain for the first year, MCloud9 goes above and beyond to deliver exceptional value.
SSD vs. HDD: The Difference Between SSD and HDD Storage (Hard Disk Drives)
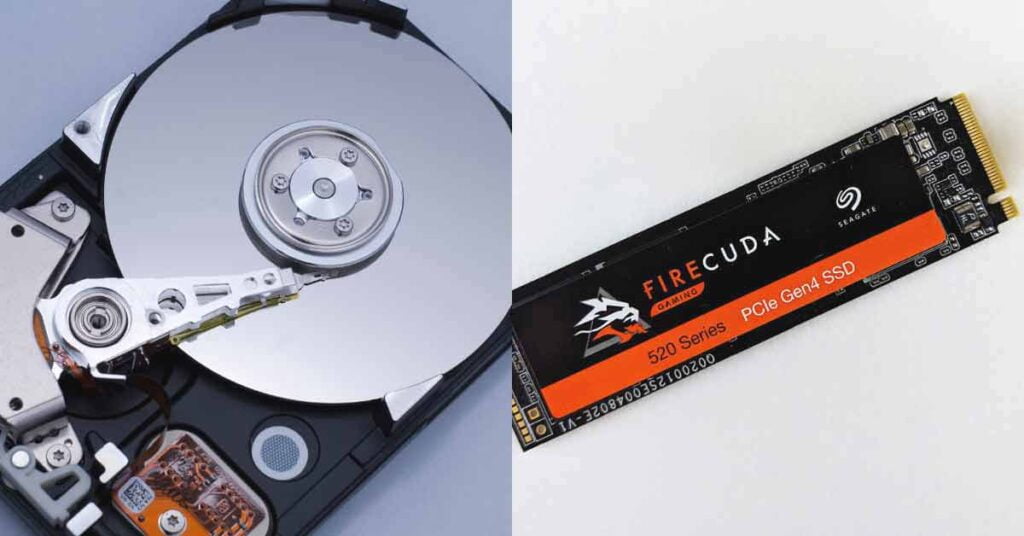

As discussed in the previous section, when comparing SSD and HDD storage, there are several key differences to consider. First and foremost, SSDs offer significantly faster data transfer speeds, enabling quicker file access and reduced waiting times. Additionally, SSDs are more resistant to shock and vibrations, making them ideal for portable devices such as laptops. Unlike HDDs, SSDs consume less power, generate less heat, and operate silently, enhancing their overall reliability and lifespan.
Pros and Cons of SSDs: Weighing the Benefits and Limitations
As with any technology, SSDs come with their own set of pros and cons. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision when considering web hosting plans. Let’s explore the advantages and limitations of SSDs:
Pros of SSDs
- Blazing Fast Performance: SSDs offer significantly faster data access and transfer speeds, resulting in improved system responsiveness and reduced loading times. This is especially beneficial for resource-intensive applications and websites with high traffic.
- Enhanced Reliability: With no mechanical parts, SSDs are less prone to mechanical failures, making them more reliable and durable than HDDs. This translates to a lower risk of data loss and a longer lifespan for your device.
- Energy Efficiency: SSDs consume less power than HDDs, contributing to reduced energy costs and environmental impact. This makes SSDs a greener choice for your web hosting infrastructure.
- Silent Operation: The absence of rotating elements in SSDs eliminates the mechanical noise associated with HDDs. This results in a quieter and more peaceful working environment.
- Compact Size: SSDs are available in various forms, including SATA, and PCIe, allowing for more flexibility in system design and space utilisation. This is particularly advantageous for small form factor devices like laptops and compact desktops.
With no mechanical parts, SSDs are less prone to mechanical failures, making them more reliable and durable than HDDs
Cons of SSDs
- Higher Cost: SSDs are generally more expensive than HDDs when comparing storage size. However, the cost per gigabyte has significantly decreased over the years, making SSDs more affordable for a wider range of users.
- Limited Lifespan: While SSDs are highly durable, they have a finite number of write cycles. However, modern SSDs employ advanced wear levelling algorithms and technologies that mitigate this limitation, ensuring a longer lifespan.
- Storage Size: Although SSDs are available in large storage capacities, they still fall behind HDDs in terms of sheer storage space. If you require vast amounts of storage for archival purposes, HDDs might be a more cost-effective option.
- Read/Write Speed Degradation: Over time, the performance of SSDs may slightly degrade due to wear and the nature of flash-based memory. However, modern SSDs employ sophisticated technologies like TRIM and garbage collection to mitigate this performance degradation.
The advantages of faster performance, reliability, energy efficiency, and silent operation make SSDs an attractive choice for website owners.
How Are SSDs Made: A Look Into the Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of SSDs involves several intricate steps that transform raw materials into high-performance storage units. Let’s take a closer look at how SSDs are made:
- NAND Flash Memory Production: The foundation of SSDs lies in NAND flash memory, a type of non-volatile storage technology. The manufacturing process begins with the production of NAND memory chips. These chips are made from silicon wafers, which undergo several processes like lithography, etching, and doping to create the transistors that store data.
- Memory Chip Assembly: Once the NAND chips are manufactured, they are assembled onto a printed circuit board (PCB). The chips are soldered onto the PCB using advanced techniques, ensuring proper electrical connections.
- Controller Integration: The controller is a crucial component of an SSD that manages data transfer, error correction, and wear levelling. The controller chip is integrated onto the SSD’s PCB, enabling communication between the NAND flash-based storage and the host system.
- Firmware Installation: SSDs have firmware, which is software embedded in the controller chip. Firmware provides instructions and algorithms that optimise the performance, reliability, and functionality of the SSD. During the manufacturing process, the firmware is installed onto the controller chip.
- Final Assembly and Testing: Once all the components are integrated, the SSD undergoes final assembly. This includes the enclosure, connectors, and any additional features specific to the SSD model. After assembly, the SSD undergoes rigorous testing to ensure functionality, performance, and compatibility with various systems.
It’s worth noting that the manufacturing process may vary slightly depending on the specific type of SSD and the manufacturer’s processes. However, the fundamental steps involved in creating an SSD remain consistent.
By understanding the manufacturing process, you can appreciate the intricate technology and craftsmanship that goes into producing these advanced storage units. SSDs have come a long way since their inception, and their manufacturing process continues to evolve, enabling even faster, more reliable, and higher-capacity SSDs to enter the market.
Different Types of SSDs: Understanding SSD Form Factors and Types
SSDs come in various form factors and types, each designed to suit different applications and systems. Let’s explore the different types of SSDs and their key characteristics:
- 2.5-Inch SATA SSDs: These SSDs feature a 2.5-inch size and shape, resembling traditional ‘hard drives’ (HDDs). They are compatible with standard drive bays found in desktop computers and laptops. SATA SSDs connect to the motherboard using a SATA interface, offering faster speeds and improved performance compared to HDDs.
- M.2 SSDs: M.2 SSDs are small and compact, ideal for ultrabooks, laptops, and small desktops. They utilise the M.2 form factor, which connects directly to the motherboard using the M.2 slot. M.2 SSDs can employ either SATA or NVMe interfaces, with NVMe offering significantly faster speeds.
- PCIe SSDs: PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) SSDs leverage the PCIe interface, providing even higher data transfer rates compared to SATA and M.2 SSDs. They are commonly used in high-performance systems, such as gaming rigs and workstations, where speed is paramount.
- NVMe SSDs: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs utilise the NVMe protocol, specifically designed for flash-based memory storage. NVMe SSDs offer exceptional speed and performance, significantly outperforming SATA-based SSDs. They are commonly found in high-end systems that demand fast data storage and retrieval.
- External SSDs: External SSDs provide portable and convenient storage solutions. These SSDs often come in compact and rugged enclosures, making them resistant to shocks and vibrations. External SSDs connect to computers and devices using interfaces like USB or Thunderbolt, allowing for easy data transfer.
- Enterprise SSDs: Enterprise SSDs are designed for data centres and enterprise-level applications that require maximum performance, reliability, and endurance. These SSDs often feature higher capacities, advanced error correction mechanisms, and robust durability to handle demanding workloads.
It’s important to consider the specific requirements of your system or application when choosing the right type of SSD. Factors such as physical dimension, interface, capacity, and intended usage should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
FAQ for What Is SSD Storage
What is SSD storage?
SSD storage refers to the use of solid state drives (SSDs) as a type of storage device used in computers and electronic devices. SSDs utilise flash memory technology, providing faster data access and transfer speeds compared to hard disk drives (HDDs). SSDs serve as the primary storage device in most modern computers.
What’s the difference between an SSD and an HDD?
SSD storage differs from HDD storage in terms of technology and performance. SSDs use flash memory to store data, whereas HDDs rely on spinning platters and magnetic read/write heads. The speed of an SSD is significantly faster due to the fact that an SSD has no moving parts, which means that data is stored and retrieved much more quickly than with an HDD. SSDs also provide improved reliability and lower power consumption compared to HDDs.
Are SSDs more expensive than HDDs?
SSDs are generally more expensive than HDDs when comparing storage size. However, the cost per gigabyte of SSDs has decreased over the years, making them more affordable. The benefits of SSDs, such as improved performance and reliability, often justify the higher cost for many users. The best SSD for you will depend on your specific needs and your budget.
Can I replace my HDD with an SSD?
Yes, you can replace your HDD with an SSD in most computers and laptops. Upgrading to an SSD can provide a noticeable performance boost, reducing boot times, and improving overall system responsiveness. It’s recommended to clone or transfer your data from the HDD to the SSD during the replacement process.
How long do SSDs last?
The lifespan of an SSD depends on various factors, including the quality of the SSD, usage patterns, and the amount of data written to it. Modern SSDs can last for many years, and most come with warranties that cover a certain number of terabytes written (TBW) or a specific duration.
Can SSDs be used for gaming?
Yes, SSDs are highly recommended for gaming due to their faster load times and improved performance. Games installed on an SSD will launch quicker, load levels faster, and provide a smoother gaming experience.
Can I use an SSD as external storage?
Absolutely! External SSDs provide portable and high-speed storage solutions. They connect to computers and devices using interfaces like USB or Thunderbolt, allowing for easy data transfer and backup.
In Conclusion

Solid-state drives (SSDs) have revolutionised storage technology, offering faster data access, improved reliability, and energy efficiency compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). We explored the history of SSDs, discussed the differences between SSDs and HDDs, and delved into the manufacturing process.
We also covered various types of SSDs, including 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, M.2 SSDs, PCIe SSDs, NVMe SSDs, external SSDs, and enterprise SSDs. SSD storage provides faster access times, quicker data transfers, and enhanced system performance.
Embracing SSD storage is a wise investment for entrepreneurs, web developers, and technology enthusiasts seeking optimal performance and reliability. With MCloud9’s reliable web hosting services, you can take advantage of SSD storage, along with other features like free SSL certificate, cPanel control panel, LiteSpeed web server, and Cloudlinux OS.
Unlock a new level of speed, efficiency, and reliability in your online presence with MCloud9’s SSD-powered web hosting services. Don’t settle for sluggish performance. Explore our hosting plans and take your digital presence to the next level.